There has been a huge controversy over “Bots as UI”: the ability to provide service to customers through Chat Bots.
Can you use Chat bots on WeChat? How do they work? What are some good examples of successful WeChat bots? Let’s look into it.
A look toward the West
Facebook Messenger has been making a lot of fuss over its bots integration. Let’s have a look at a few “famous” Facebook Messenger bots.
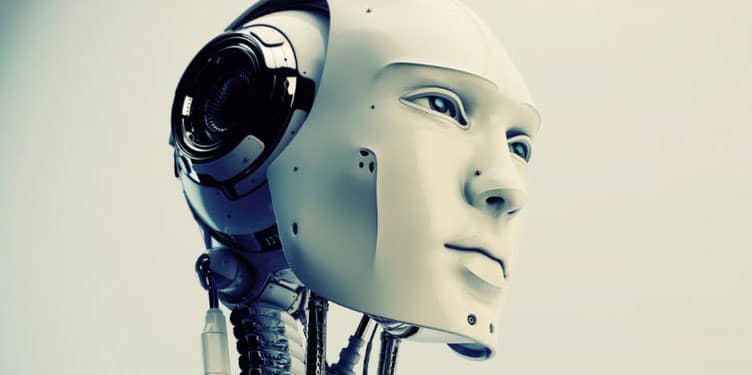
Sure: a food & drink bot
Sure is an equivalent of the “Food and drinks” capabilities of Siri. You can ask it about restaurants and bars in your surroundings.
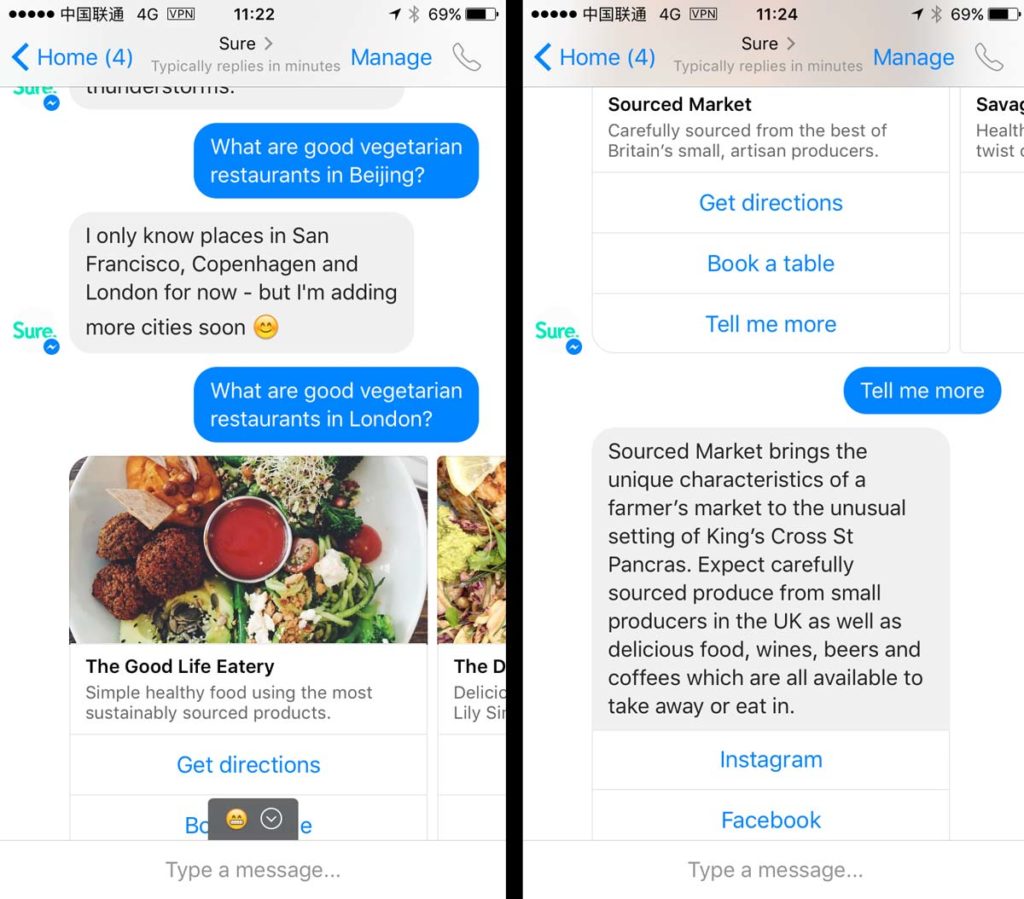
1-800-flowers.com bot
The messenger bot of 1-800-flowers bot enables you to order flowers… through a very lengthy and unintuitive process.
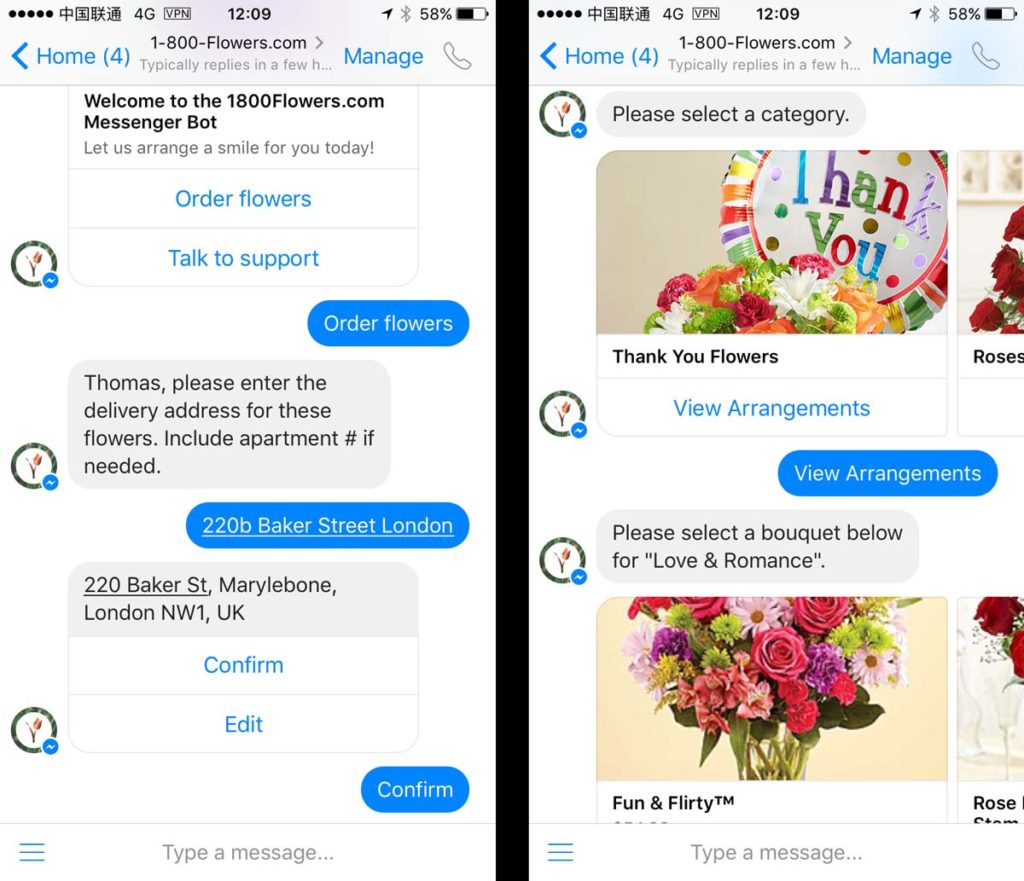
Poncho the weathercat… tells you the weather
Weather bots might be the most classic form of chat bots. The input and output are very standardized, so it’s easy for the bot to understand the question and provide a correct answer.
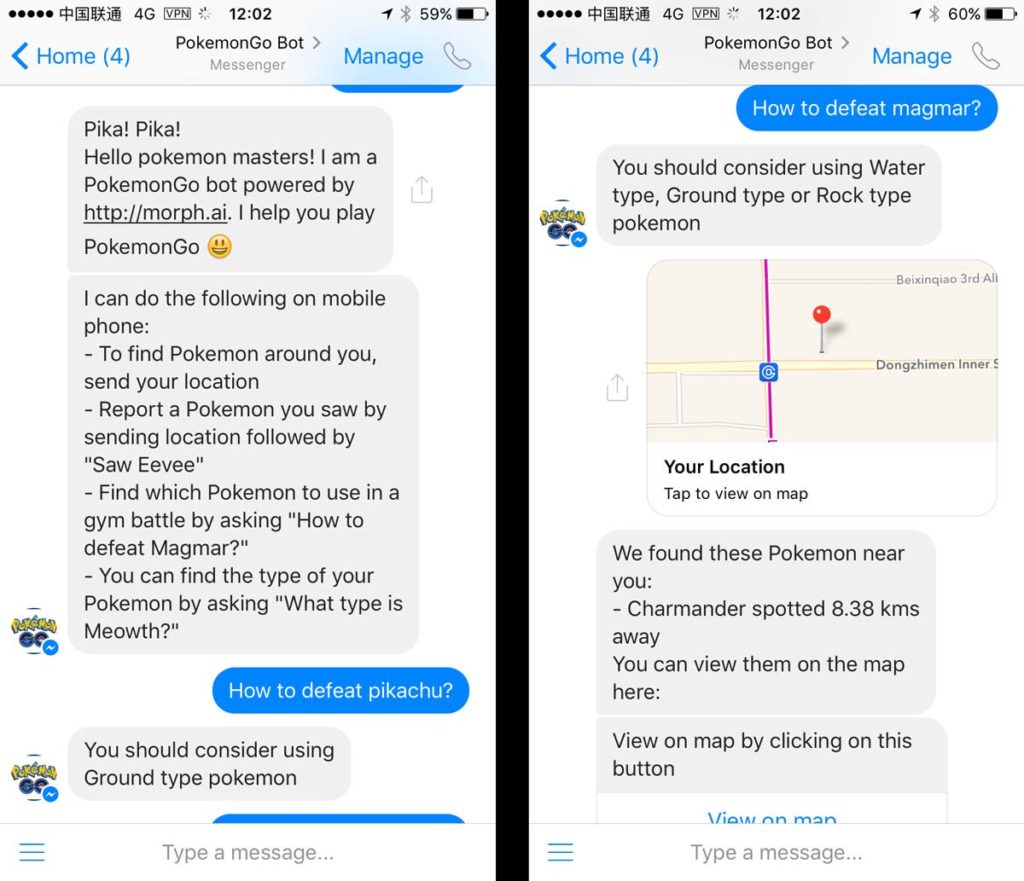
The Pokemon GO bot
The new rule of the Internet: for any list of things on the Internet, there is a Pokemon version of it. And there is, of course, a Pokemon messenger bot enabling you to locate Pokemons and know how to defeat them.
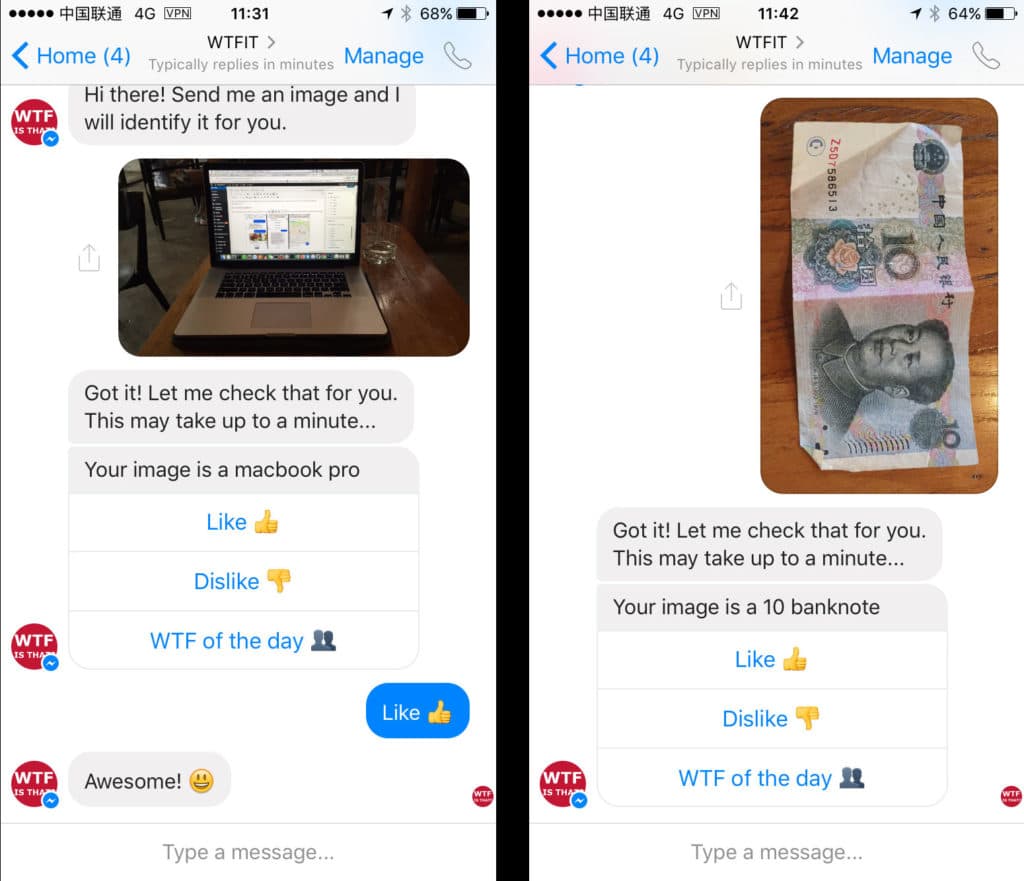
WTFIT: the bot that recognizes stuff
Other types of bots are utterly useless but are just here to showcase the possibilities behind A.I. That’s the case for WTFIT (standing for: “What the fuck is that?”), which can recognize objects if you send it a picture.
How do these bot work?
When we think of chat bots, we usually think of them as we think of humans. We expect them to be able to carry a “normal” conversation (what we call “general intelligence), and we think of their “brains” like we think of ours. A network of neurons is enabling them to make decisions and give intelligent answers.
Well, that’s not at all how bots work.
Most bots, including most Facebook Messenger bots, look much more like this:
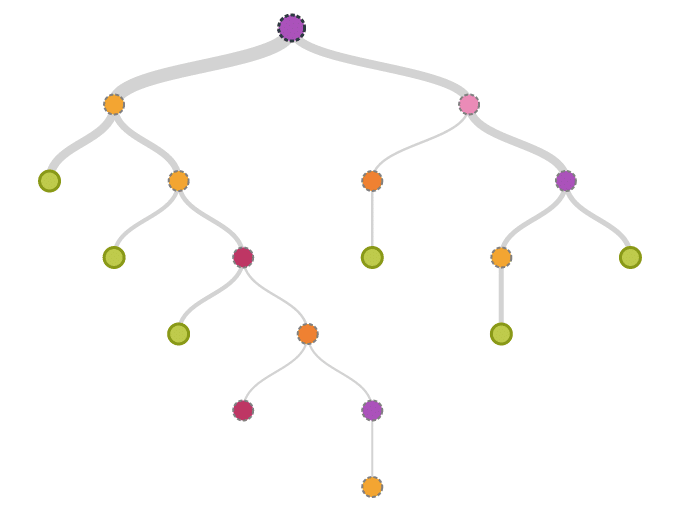
That is, most bots today work through decision trees. They will use more advanced forms of artificial intelligence (deep learning / neural networks) to study the messages sent by a user. But at the end of the day, you can only tell the bot which patterns to recognize, and which answer to give for a particular pattern. The bot isn’t going to get “creative” at any point.
This way of functioning has substantial implications: it means a bot can only operate in a very narrow context where you took the time to pre-define the right answers to specific, expected questions.
So, when are bots useful?
The architecture above means that bots have significant limitations. They can’t be carelessly thrown around to replace any existing User Interface.
So, when are bots a good UI choice?
#1. Narrow scope of expertise
As we mentioned earlier, bots are working through decision trees, and their answers must be to a large extent pre-defined. You can’t expect a bot, as of today, to have “general intelligence” and hold an elaborate conversation. So you must set a clearly defined scope of expertise for your bot (the weather, restaurant listings in certain cities, etc.)
#2. Wide range of inputs
Bots don’t make sense if the diversity of inputs is very limited. Let’s say I want to top-up my phone: would it make sense to do so via a bot? Not really, as there is only one input here: the top-up amount. A simple click is enough, no need to get into a long conversation which could create more problems than it will solve.
However, if I am trying to find a restaurant, there might be a lot of parameters involved. I might be looking for a vegetarian restaurant in Beijing, which isn’t too expensive and open after 9 pm. Natural language processing (the ability of bots to understand what we say and turn it into machine-readable information) can be a great way for a bot to give me a quick answer.
#3. Constantly evolving output
Another asset of bots is their evolving nature. Every day, you can review the requests from customers and enhance the answers to make them more exhaustive. If your client is merely trying to order flowers or pizza, a bot might not add a lot of value. But if you are talking about customer service, having an open chat window might help a lot: customers are not constrained by the user interface you set for them.
For simple questions, the bot might be able to answer. If it can’t, a customer service representative will take over. And over time, the bot will get smarter and smarter and learn to handle more sophisticated requests by itself.
Chatbots and China
China already saw a few successful chatbots implementations. Major Chinese tech companies are also building tools to support a “chatbot revolution”.
The Alibaba chatbot
A great illustration of the above principles is the Alibaba chatbot. Like Facebook bots, it is using a combination of “free input” from users and multiple choice answers. If the bot is unsure about what you just said, it might offer you several options to pick from.

By taking this hybrid approach, the Alibaba bot can both provide a value added service, while keeping a flexible and evolving approach to customer service.
Chumen Wenwen
We covered in a previous article the company Chumen Wenwen. The startup, created by former Google engineers and backed by the prestigious VC firm Sequoia Capital, developed its proprietary voice recognition software for Chinese and integrated it to both a WeChat account and its native APP.
The APP works like a Chinese equivalent on Siri, and the company is now releasing wearables integrating their voice recognition software.
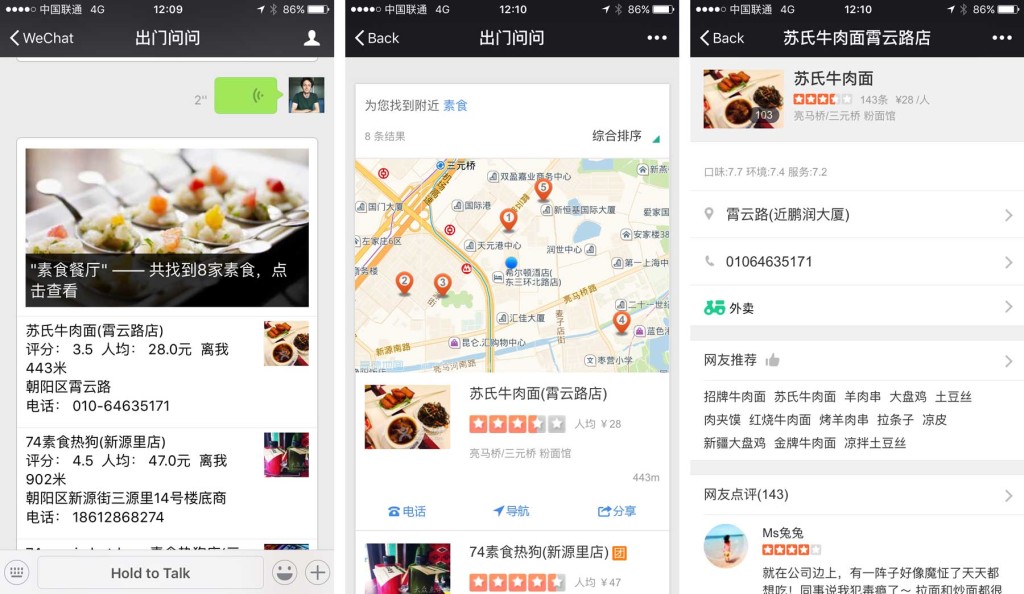
What are BAT (Baidu, Alibaba, Tencent) doing about Chatbots?
We already talked about Alibaba and its popular chat bot.
The rest of BAT (Baidu and Tencent) are not forgetting about chatbots and their potential. Both of the companies provide services for “Natural language processing” enabling to create your own bots (because if the workflow of the bot itself might be a simple decision tree, being able to correctly process human-written text is a complex A.I problem. That’s where Baidu and Tencent can help).
The Tencent platform (http://nlp.qq.com/) offers interesting examples, including sentiment analysis on any Chinese text you enter in their demo box, and even being able to understand the main topics brought up in a short paragraph (try it here) .
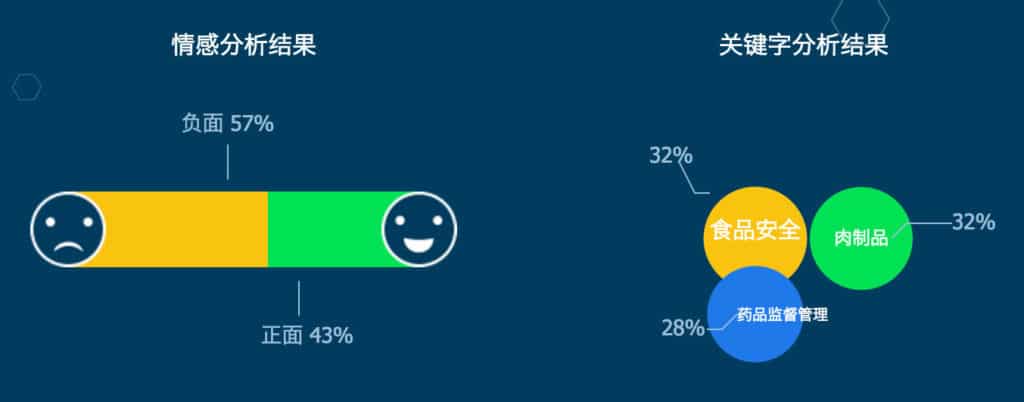
These tools make it easy for developers to create their own bots, even with a very limited initial knowledge of bots and artificial intelligence.
Conclusion
Chat bots are by no mean a silver bullet which will replace all existing UI. However, as they get more sophisticated, there are more and more use-cases for them, and customer service is one of them.
With big companies like Facebook and Tencent stepping up to provide API’s, and leveraging on the large amount they collect, it is now possible for developers to build useful bots creating value for customers and for their organizations.